Set
首先引入Set。
无序性
- Set集合类似于一个罐子,程序可以依次把多个对象“丢进”Set集合,而Set集合通常不能记住元素的添加顺序。
互异性
- Set集合不允许包含相同的元素。
- 如果试图把两个相同元素加入同一个Set集合中,则添加操作失败,add()方法返回false,且新元素不会被加入。
接口特性
- 因为其是一个抽象的接口,所以不能直接实例化一个set对象。Set s = new Set() 会报错。
- 该接口主要继承于Collections接口,所以具有Collection的一些常见的方法。
Set接口最常用的两大实现:HashSet和TreeSet。
TreeSet
TreeSet是一个有序集合,它扩展了AbstractSet类并实现了NavigableSet接口。
TreeSet有如下特点:
- 它存储唯一的元素
- 它不保留元素的插入顺序
- 它按升序对元素进行排序
- 它不是线程安全的
1 继承关系
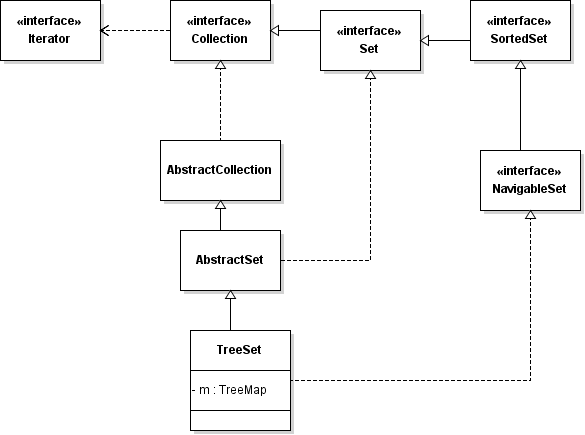
类图标记说明

从图中可以看出:
- TreeSet继承于
AbstractSet,并且实现了NavigableSet接口。 - TreeSet的本质是一个"
有序的,并且没有重复元素"的集合,它是通过TreeMap实现的。
TreeSet中含有一个"NavigableMap类型的成员变量"m,而m实际上是"TreeMap的实例"。
2 代码理解
接下来通过编写代码的形式切身体会TreeSet的用法及特点。
2.1 创建元素
定义一个名为Gun的类用以存储枪械的名称、威力、射速及价格等属性,后续操作以此类为基础实现。
public class Gun {
private String name; // The name of the gun.
private int power; // The power of the gun.
private int firingRate; // The firing rate of the gun.
private int price; // The price of the gun.
// The constructor with no parameters.
public Gun() {}
// The constructor with the gun's name.
public Gun (String name) {
this.name = name;
}
// The constructor with all attributes of the gun.
public Gun (String name, int power, int firingRate, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.power = power;
this.firingRate = firingRate;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public int getPower() {
return this.power;
}
public int getFiringRate() {
return this.firingRate;
}
public int getPrice() {
return this.price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Name:" + this.name + "\t\t" +
"Power:" + this.power + "\t\t" +
"Firing Rate:" + this.firingRate + "\t\t" +
"Price:" + this.price;
}
}2.2 创建实例
2.2.1 构造方式
由于TreeSet的有序性及互异性,在TreeSet的内部会有一个用于排序及除重的元素比较机制,即比较器。
而TreeSet有无参构造和带参构造两种构造方式,这里的参数指的就是比较器。
2.2.2 无参构造(自然排序)
如果我们的元素是Integer这样能够直接进行比较的数据类型,就可以采用下面这种无参构造的方式,TreeSet会让元素所属的类实现自然排序接口Comparable,即默认排序。
Set<Integer> set1 = new TreeSet<>();
SortedSet<Integer> set2 = new TreeSet<>();
TreeSet<Integer> set3 = new TreeSet<>();而在本例中我们的元素是一个自定义对象Gun,采用默认排序无法实现元素的排序,我们便有两种方式来解决这个问题。
2.2.3 无参构造(重写compareTo)
这仍是一种无参构造的构造方式,原理是在Gun类中重写compareTo函数来让元素具备可比较性。
例如我们可以根据枪械的价格进行排序:
public class Gun implements Comparable<Gun> {
@Override
public int compareTo(Gun o) {
return this.price - o.price;
}
}2.2.3 带参构造(定制排序)
我们也可以通过创建一个比较器接口的子类对象GunComparator来实现带参构造,这样类中的元素就可以根据该接口的方法来排序。
import java.util.Comparator;
public class GunComparator implements Comparator<Gun> {
private final String sortBy; // The sort by.
public GunComparator() {
this.sortBy = " ";
}
public GunComparator(String sortBy) {
this.sortBy = sortBy;
}
public int compare(Gun firstGun, Gun secondGun) {
return switch (sortBy) {
case "Power" -> firstGun.getPower() - secondGun.getPower();
case "Firing Rate" -> firstGun.getFiringRate() - secondGun.getFiringRate();
case "Price" -> firstGun.getPrice() - secondGun.getPrice();
// The default sort by is sorting elements by comparing names.
default -> firstGun.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(secondGun.getName());
};
}
}在该方法中我们构造了一个含参构造器,使得我们可以根据枪械的任何一种属性来进行排序。
于是我们可以使用此方法来构造一个TreeSet,TreeSet就会根据枪械的名称属性来比较元素。
Set<Gun> ARSENAL = new TreeSet<>(new GunComparator());2.3 添加元素
2.3.1 TreeSet add()
add()方法可以将元素添加到一个TreeSet中,添加成功返回true,否则返回false。
System.out.println("\nDemo_1");
Gun awp1 = new Gun("AWP", 115, 41, 4750);
Gun awp2 = new Gun("AWP", 115, 41, 4750);
Gun awp3 = new Gun("AWPRO", 115, 41, 4750);
System.out.println("Add awp1: " + ARSENAL.add(awp1)); // true
System.out.println("Add awp2: " + ARSENAL.add(awp2)); // false
System.out.println("Add awp3: " + ARSENAL.add(awp3)); // true输出结果为:
Demo_1
Add awp1: true
Add awp2: false
Add awp3: true
2.3.2 除重
无论是除重还是排序,都依靠TreeSet的比较器来实现。
这也是对AWP的第二次添加失败的原因。
让我们定位到比较器的compare()方法。
public int compare(Gun firstGun, Gun secondGun) {
return switch (sortBy) {
case "Power" -> firstGun.getPower() - secondGun.getPower();
case "Firing Rate" -> firstGun.getFiringRate() - secondGun.getFiringRate();
case "Price" -> firstGun.getPrice() - secondGun.getPrice();
// The default sort by is sorting elements by comparing names.
default -> firstGun.getName().compareToIgnoreCase(secondGun.getName());
};
}在该switch语句中,对int类型的两个元素进行了减法,而对String类型的两个元素使用了compareToIgnoreCase()方法,因此我们不难推出其结论:当两元素大小不同时,将会返回一个正数或负数,TreeSet就会根据这个数的符号进行排序,例如如果返回的是一个负数,firstGun就会排在secondGun的前面,反之亦然。但如果返回的是0,那么TreeSet的互异性就会在此展示出来,除第一次以外的添加都会失败。
2.4 遍历方式
TreeSet的遍历方式主要有三种。
System.out.println("\nDemo_2");
System.out.println(ARSENAL);
System.out.println("\==============================");
Iterator<Gun> iterator = ARSENAL.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(iterator.next());
}
System.out.println("\==============================");
for (Gun gun : ARSENAL) {
System.out.println(gun);
}第一种:直接输出该集合
第二种:使用迭代器遍历
第三种:使用增强for循环遍历
输出结果如下:
Demo_2
[Name:AWP Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750, Name:AWPRO Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750]
==============================
Name:AWP Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750
Name:AWPRO Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750
==============================
Name:AWP Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750
Name:AWPRO Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750
2.5 排序方式
由于我们在GunComparator接口中定义了一个含参构造器,我们就可以利用这个构造器根据不同的需求进行不同依据的排序。
先搞一个文本文档存储测试数据:
Nova 243 68 1050
MAG-7 240 71 1300
MP9 26 857 1250
MP7 29 750 1500
AK-47 36 600 2700
M4A4 33 666 3100
AUG 28 600 3300
AWP 115 41 4750
G3SG1 80 240 5000
Negev 35 800 1700
再写一个读取数据和遍历输出的方法:
public void fill() {
try {
Scanner gunParams = new Scanner(new File(".\\TestingData\\guns.txt"));
while (gunParams.hasNext()) {
StringTokenizer gunParamsTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(gunParams.nextLine());
Gun gun = new Gun(gunParamsTokenizer.nextToken(),
Integer.parseInt(gunParamsTokenizer.nextToken()),
Integer.parseInt(gunParamsTokenizer.nextToken()),
Integer.parseInt(gunParamsTokenizer.nextToken()));
ARSENAL.add(gun);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}public void print() {
for (Gun gun : ARSENAL) {
System.out.println(gun);
}
}最后写一个demo3进行测试:
System.out.println("\nDemo_3");
System.out.print("SortBy: ");
String sortBy = new Scanner(System.in).nextLine();
ARSENAL = new TreeSet<>(new GunComparator(sortBy));
fill();
print();输入指定的排序依据就会根据此依据进行排序,这里以射速(Firing Rate)为例:
Demo_3
SortBy:Firing Rate
Name:AWP Power:115 Firing Rate:41 Price:4750
Name:Nova Power:243 Firing Rate:68 Price:1050
Name:MAG-7 Power:240 Firing Rate:71 Price:1300
Name:G3SG1 Power:80 Firing Rate:240 Price:5000
Name:AK-47 Power:36 Firing Rate:600 Price:2700
Name:M4A4 Power:33 Firing Rate:666 Price:3100
Name:MP7 Power:29 Firing Rate:750 Price:1500
Name:Negev Power:35 Firing Rate:800 Price:1700
Name:MP9 Power:26 Firing Rate:857 Price:1250
2.6 其它常用函数
2.6.1 TreeSet contains()
contains()方法被用来检查一个给定的元素是否存在于一个给定的TreeSet中。
如果找到该元素,则返回true,否则返回false。
Gun desertEagle = new Gun("Desert Eagle", 63, 267, 700);
System.out.println("Contains " + desertEagle.getName() + ":" + ARSENAL.contains(desertEagle)); // false
ARSENAL.add(desertEagle);
System.out.println("Contains " + desertEagle.getName() + ":" + ARSENAL.contains(desertEagle)); // true输出结果为:
Contains Desert Eagle :false
Contains Desert Eagle :true
2.6.2 TreeSet remove()
remove()方法用于从该集合中删除指定的元素,如果它存在。
如果删除成功,则此方法返回true。
ARSENAL.remove(desertEagle);
System.out.println("Contains " + desertEagle.getName() + ":" + ARSENAL.contains(desertEagle)); // false输出结果为:
Contains Desert Eagle:false
2.6.3 TreeSet clear()
如果我们想要从集合中删除所有项,可以使用clear()方法。
2.6.4 TreeSet size()
size()方法被用于识别存在于该TreeSet中元素的数量。
它是API中的基本方法之一。
2.6.5 TreeSet isEmpty()
isEmpty()方法可用于判断一个给定的TreeSet是否为空。
System.out.println("Size:" + ARSENAL.size());
System.out.println("If empty:" + ARSENAL.isEmpty());
ARSENAL.clear();
System.out.println("Size:" + ARSENAL.size());
System.out.println("If empty:" + ARSENAL.isEmpty());输出结果为:
Size:10
If empty:false
Size:0
If empty:true
2.6.6 其它函数
TreeSet first()
- 如果TreeSet不为空,则此方法返回TreeSet中的第一个元素。否则,它会抛出NoSuchElementException。
TreeSet last()
- 与上面的示例类似,如果集合不为空,此方法将返回最后一个元素。
TreeSet subSet()
- 此方法将返回从fromElement到toElement的元素。
- fromElement是包含的,toElement是不包含的。
TreeSet headSet()
- 此方法将返回TreeSet的元素,这些元素小于指定的元素。
TreeSet tailSet()
- 此方法将返回TreeSet的元素,这些元素大于或等于指定的元素。
2.7 存储空元素
在Java 7之前,可以将空元素添加到空TreeSet中。
但是,这被认为是一个错误。因此,TreeSet不再支持添加null。
当我们向TreeSet添加元素时,元素将根据其自然顺序或比较器指定的方式进行排序。因此,与现有元素相比,添加null会导致NullPointerException,因为null无法与任何值进行比较。
插入TreeSet的元素必须实现Comparable接口,或者至少被指定的比较器接受。所有这些元素必须是可相互比较的, 即 e1.compareTo(e2)或comparator.compare(e1,e2)不得抛出ClassCastException。
3 性能
与HashSet相比,TreeSet的性能更低。
添加、删除和搜索需要O(log n)的时间,而打印有序元素则需要O(n)的时间。
4 结论
- TreeSet实际上是由TreeMap实现的,而TreeMap是由红黑树实现的。
- TreeSet支持自然排序和定制排序两种排序方式。
- TreeSet具有互异性,存储的元素唯一。
- TreeSet不允许放入null值。
- 相比于HashSet,TreeSet的性能较低,但其拥有有序性的优点。
参考资料: